概述
Java NIO 全称 java non-blocking IO,是指 JDK 提供的新 API。从 JDK1.4 开始,Java 提供了一系列改进的输入/输出的新特性,被统称为 NIO(即 New IO),是同步非阻塞的。
NIO 三大核心部分:Channel(通道),Buffer(缓冲区), Selector(选择器)。
NIO 是面向缓冲区,或者面向块编程的。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动,这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性,使用它可以提供非阻塞式的高伸缩性网络。
Java NIO 的非阻塞模式,使一个线程从某通道发送请求或者读取数据,但是它仅能得到目前可用的数据,如果目前没有数据可用时,就什么都不会获取,而不是保持线程阻塞,所以直至数据变的可以读取之前,该线程可以继续做其他的事情。非阻塞写也是如此,一个线程请求写入一些数据到某通道,但不需要等待它完全写入, 这个线程同时可以去做别的事情。
NIO 和 BIO 的比较
- BIO 以流的方式处理数据,而 NIO 以块的方式处理数据,块 I/O 的效率比流 I/O 高很多
- BIO 是阻塞的,NIO 则是非阻塞的
- BIO 基于字节流和字符流进行操作,而 NIO 基于 Channel(通道)和 Buffer(缓冲区)进行操作,数据总是从通道读取到缓冲区中,或者从缓冲区写入到通道中。Selector(选择器)用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接请求,数据到达等),因此使用单个线程就可以监听多个客户端通道
工作机制
示意图
NIO 简单原理示意如下图所示:
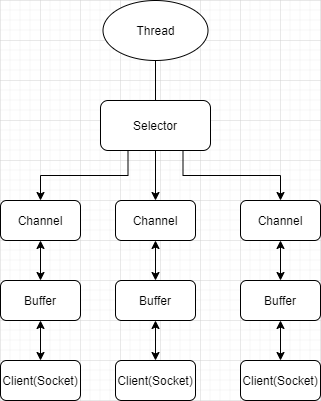
- Buffer 是内存块,底层是数组,数据的读取写入通过Buffer ,Buffer 可以读也可以写,需要flip 方法切换
- Channel 是双向的,可以反映底层操作系统的情况,比如Linux 底层的操作系统通道就是双向的,每个Channel 都会对应一个Buffer
- Selector 对应一个线程,一个线程对应多个Channel(连接),Selector 会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换
缓冲区 Buffer
缓冲区(Buffer):缓冲区本质上是一个可以读写数据的内存块,可以理解成是一个容器对象(含数组),该对象提供了一组方法,可以更轻松地使用内存块,缓冲区对象内置了一些机制,能够跟踪和记录缓冲区的状态变化情况。Channel 提供从文件、网络读取数据的渠道,但是读取或写入的数据都必须经由 Buffer。
Buffer 类内部结构如下:
1
2
3
4
| private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;
|
Buffer 类相关方法一览:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public final int capacity()
public final int position()
public final Buffer position(int newPosition)
public final int limit()
public final Buffer limit(int newLimit)
public final Buffer mark()
public final Buffer reset()
public final Buffer clear()
public final Buffer flip()
public final Buffer rewind()
public final int remaining()
public final boolean hasRemaining()
public boolean isReadOnly()
public boolean hasArray()
public Object array()
public int arrayOffset()
public boolean isDirect()
|
Java 中的基本数据类型(boolean除外),都有Buffer 实现类,其中最常用的是ByteBuffer (二进制数据),该类主要方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public static ByteBuffer allocateDirect(int capacity)
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity)
public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array)
public static ByteBuffer wrap(byte[] array, int offset, int length)
public byte get()
public byte get(int index)
public ByteBuffer put(byte b)
public ByteBuffer put(int index, byte b)
|
通道 Channel
NIO 的通道(Channel)类似于流(stream,如FileInputStream),但有些区别如下:
- 通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写
- 通道可以实现异步读写数据
- 通道可以从缓冲读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲
Channel 是一个接口,常用的Channel 类有:FileChannel 、DatagramChannel 、ServerSocketChannel 和SocketChannel。(ServerSocketChannel类似ServerSocket ,SocketChannel 类似Socket)
- FileChannel 用于文件的数据读写
- DatagramChannel 用于 UDP 的数据读写
- ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 用于 TCP 的数据读写
FileChannel 类主要用来对本地文件进行IO 操作,常用方法有:
1
2
3
4
| public int read(ByteBuffer dst)
public int write(ByteBuffer src)
public long transferFrom(ReadableByteChannel src, long position, long count)
public long transferTo(long position, long count, WritableByteChannel target)
|
应用示例
文件读取、写入
使用Channel、Buffer将文件1中的内容写入到文件2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class FileChannelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("1.txt");
FileChannel inFileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("2.txt");
FileChannel outFileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while(true) {
buffer.clear();
int read = inFileChannel.read(buffer);
if (read == -1) {
break;
}
buffer.flip();
outFileChannel.write(buffer);
}
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
|
拷贝文件 transferFrom 方法
使用 FileChannel和方法transferFrom 完成文件的拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class FileChannelDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("a.png");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("b.png");
FileChannel sourceCh = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel destCh = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh,0,sourceCh.size());
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
|
注意事项
- ByteBuffer 支持类型化的put 和get,put 放入的是什么数据类型,get就应该使用相应的数据类型来取出
- 可以将普通Buffer 转成只读Buffer,asReadOnlyBuffer()
- NIO 还提供了 MappedByteBuffer,可以让文件直接在内存(堆外内存)中进行修改,而如何同步到文件由 NIO 来完成
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class MappedByteBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("1.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer mappedByteBuffer = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
mappedByteBuffer.put(0, (byte) 'A');
mappedByteBuffer.put(3, (byte) 'B');
randomAccessFile.close();
}
}
|
- NIO 还支持 通过多个Buffer (即 Buffer 数组) 完成读写操作,即 Scattering 和 Gathering
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
public class ScatteringAndGatheringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
int messageLength = 8;
while (true) {
int byteRead = 0;
while(byteRead < messageLength) {
long length = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead += length;
System.out.println("byteRead=" + byteRead);
Arrays.stream(byteBuffers)
.map(buffer -> "position=" + buffer.position() + ", limit=" + buffer.limit())
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::flip);
long byteWrite = 0;
while (byteWrite < messageLength) {
long length = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += length;
}
Arrays.asList(byteBuffers).forEach(Buffer::clear);
System.out.println("byteRead=" + byteRead + ", byteWrite=" + byteWrite + ", messageLength=" + messageLength);
}
}
}
|
选择器 Selector
Selector 能够检测多个注册的通道上是否有事件发生(注意:多个Channel 以事件的方式可以注册到同一个Selector),如果有事件发生,便获取事件然后针对每个事件进行相应的处理。这样就可以只用一个单线程去管理多个通道,也就是管理多个连接和请求。
只有在 连接/通道 真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写,就大大地减少了系统开销,并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护多个线程。避免了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销。
Selector 类是一个抽象类, 常用方法和说明如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public static Selector open()
public Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys()
public int select(long timeout)
public int select()
public int selectNow()
public Selector wakeup()
|
NIO 非阻塞网络编程原理分析
NIO 非阻塞 网络编程相关的(Selector、SelectionKey、ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel) 关系梳理图如下:
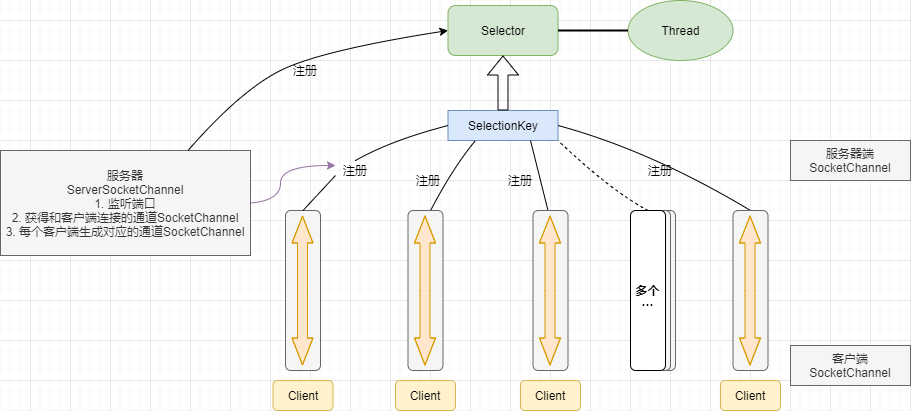
- 当客户端连接时,会通过 ServerSocketChannel 得到 SocketChannel
- Selector 进行监听 select 方法, 返回有事件发生的通道的个数
- 将 socketChannel 注册到 Selector 上, register(Selector sel, int ops), 一个 selector 上可以注册多个 SocketChannel
- 注册后返回一个 SelectionKey, 会和该 Selector 关联(集合)
- 进一步得到各个 SelectionKey (有事件发生)
- 在通过 SelectionKey 反向获取 SocketChannel , 方法 channel()
- 通过得到的 channel , 完成业务处理
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
|
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
Selector selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
if (selector.select(1000) == 0) {
System.out.println("服务器等待1s, 无连接");
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("客户端已连接, socketChannel: " + socketChannel.hashCode());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println("客户端消息: " + new String(buffer.array()));
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)) {
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("因为连接需要时间, 客户端不会阻塞, 可以做其它工作...");
}
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello nio server".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(buffer);
System.in.read();
}
}
|
SelectionKey
SelectionKey 表示 Selector 和网络通道的注册关系, 共四种:
1
2
3
4
| public static final int OP_READ = 1 << 0;
public static final int OP_WRITE = 1 << 2;
public static final int OP_CONNECT = 1 << 3;
public static final int OP_ACCEPT = 1 << 4;
|
相关方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public Selector selector()
public SelectableChannel channel()
public final Object attachment()
public SelectionKey interestOps(int ops)
public final boolean isAcceptable()
public final boolean isReadable()
public final boolean isWritable()
|
ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel 在服务器端监听新的客户端 Socket 连接
相关方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| public static ServerSocketChannel open()
public final ServerSocketChannel bind(SocketAddress local)
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block)
public SocketChannel accept()
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops)
|
SocketChannel
SocketChannel 是网络IO通道,具体负责进行读写操作。NIO把缓冲区的数据写入通道,或者把通道里的数据读到缓冲区。
相关方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public static SocketChannel open()
public final SelectableChannel configureBlocking(boolean block)
public boolean connect(SocketAddress remote)
public boolean finishConnect()
public int write(ByteBuffer src)
public int read(ByteBuffer dst)
public final SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops, Object att)
|
案例:群聊系统
- 编写一个 NIO 多人群聊系统,实现服务器端和客户端之间的数据简单通讯(非阻塞)
- 服务器端:可以监测用户上线,离线,并实现消息转发功能
- 客户端:通过channel 可以无阻塞发送消息给其它所有用户,同时可以接受其它用户发送的消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
|
public class GroupChatServer {
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel listenerChannel;
private final int PORT = 6667;
public GroupChatServer() {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
listenerChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
listenerChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
listenerChannel.configureBlocking(false);
listenerChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void listener() {
try {
while(true) {
int count = selector.select(2000);
if (count > 0) {
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = listenerChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " 已上线");
} else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) {
readData(selectionKey);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void readData(SelectionKey selectionKey) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int count = socketChannel.read(buffer);
if (count > 0) {
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " 消息: " + msg);
sendInfo(socketChannel, msg);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress() + " 已下线");
selectionKey.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void sendInfo(SocketChannel selfChannel, String msg) {
System.out.println("开始转发消息");
try {
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {
Channel channel = key.channel();
if(channel instanceof SocketChannel && channel != selfChannel) {
((SocketChannel)channel).write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()));
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("转发完成");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GroupChatServer chatServer = new GroupChatServer();
chatServer.listener();
}
}
public class GroupChatClient {
private final String HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private final int PORT = 6667;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String username;
public GroupChatClient() {
try {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(HOST, PORT));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println(username + " 准备完毕");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void sendInfo(String msg) {
msg = username + ": " + msg;
try {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void readMsg() {
try {
int readChannels = selector.select();
if (readChannels > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.read(buffer);
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println(msg);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
GroupChatClient chatClient = new GroupChatClient();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
chatClient.readMsg();
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String s = scanner.nextLine();
chatClient.sendInfo(s);
}
}
}
|

